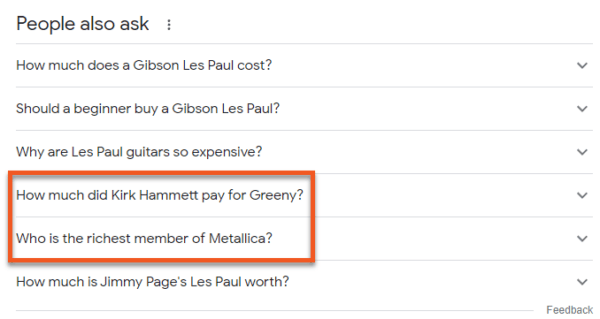In the past, publishers would optimize content for keywords to please search engines and improve rankings. As a result, the search engine results page (SERP) returned results containing poor-quality content that often failed to answer user queries.
Fast forward to today, search engines now prioritize positive user experience and ‘people-first’ content. Search engines consider content depth, meaning (aka semantics), and how it answers user questions by providing the desired information.
Businesses must adapt to this evolution of search. As search engines become more sophisticated, incorporating semantic understanding into your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy is crucial to keep up with the changing landscape. This will help ensure your content remains relevant and visible to your target audience.
Understanding Semantic SEO
The word ‘semantic’ is all about understanding the meaning of language.
When people use the term ‘arguing about semantics’, they’re usually debating the interpretation (or misunderstanding) of words or phrases. Semantics is a field that examines how language conveys meaning and follows certain rules for effective communication.
Semantic SEO is the process of giving more meaning and context to your web content to help search engines gain a better understanding of your content.
Why is Semantic SEO important?
The way that search engines understand your content has changed
Historically, Google solely used keywords to evaluate a web page’s topic and relevance to a search query. As of Google’s algorithm changes made in 2013, however, instead of only looking at keywords to understand what the page is about, search engines now read and understand a page’s overall topic.
This change allowed search engines to provide users with a better search experience and ensure that the results presented are providing users with the answers they are looking for.
To improve your ranking and web traffic
By utilizing semantic SEO, search engines can better understand your content and more accurately relate it to search queries. In return, your pages can rank higher on relevant searches, leading to more impressions and, ideally, more clicks.
Because it presents users with the most relevant information based on their queries, those who do visit your pages are more easily converted into customers. This is because it’s more likely to be exactly the information/product/service they were seeking.
To keep up with generative AI search
Semantic SEO is the future of search, and that future has already begun. The emergence of powerful generative AI search engines like Google’s Search Generative Experience, has propelled semantic technology to unprecedented heights.
In this transformative era with the AI revolution and search generative experience, search engines are gaining an unprecedented ability to interpret the nuances and meaning of human language. As a result, search queries are now returning dynamic and tailored results with the potential for conversational follow-up answers.
While traditional SEO practices, including keyword research, remain valuable in digital marketing, integrating semantic technologies like Schema Markup into your strategy can provide a competitive advantage.
By doing so, your pages become more visible and comprehensible to the intelligent systems that bridge the gap between your content and human users.
Preparing for Generative AI Search: Essential Strategies and Insights
Learn about the benefits and challenges of generative AI search engines, and three key strategies that you can take to prepare for AI search.
How is Semantic SEO Different From Traditional SEO?
Where traditional SEO prioritizes content that is keyword-based, semantic SEO is a topic-based approach that increases the likelihood of connecting users to information that is most relevant to their search query.
It accomplishes this by focusing on both the meaning behind queries and the contextual information and relationships in the content being retrieved. This results in a better user experience which can lead to a lower bounce rate, as those who end up on your page from search have a higher intent to consume the information presented.
Semantic SEO is the bridge between your content and users’ intent. This is the biggest difference between Traditional SEO and Semantic SEO. – WeDevs
Moving from a keyword-based to a topic-based approach with your content can seem a bit abstract at first. After all, it’s simple enough to do some keyword research, find a list of terms, and then write content to string the terms together.
These same skills are still essential when it comes to semantic SEO, with one key difference: entities.
What are Entities?
To put it plainly: entities are things, and things have dimensions!
They take up space (be it physical, digital, or conceptual). They also have attributes (like colour, size, duration) and, most importantly, they are understood in relation to other things.
Take, for example, “bestgihrtie”. This is a string of characters and it means nothing to a human brain, so it won’t mean anything to a search engine either. But if I decide it’s the name of my new album, snackfood, or generative AI tool, this jumble of letters now becomes an identifiable entity. In other words, the string becomes a thing.
However, that entity needs to be described for it to have any meaning. “ChatGPT” didn’t mean anything until we started hearing about it in relation to generative AI, chatbots, and productivity.
This same entity took on a different meaning when we heard about it in relation to hallucinations, misinformation, algorithmic bias, and plagiarism. The word “relation” is doing the heavy lifting in this example since what it’s providing is context.
We as humans use context clues to make sense of new things and search engines are doing the same thing.
That being said, machines, including search engines, aren’t good at understanding in the same way that human brains can. Search engines use natural language processing (NLP) to analyze the proximity and frequency of certain terms, phrases and entities.
There are ways, however, to make statements about entities more explicit for search engines.
Elevating Search with Entities
As previously stated, semantic search goes beyond traditional keyword matches and focuses on delivering topically relevant search results.
Instead of simply providing “plain blue links” to web pages, it can present information in various formats, such as Knowledge Panels, Featured Snippets, and Rich Results, all centered around the primary entity being searched.
This approach aims to provide users with more comprehensive and contextually relevant information related to their search query. Let’s look at an example of how a search for “Gibson Les Paul” yields results about this particular entity.
Under the “People also ask” section, we can see queries that don’t blatantly name the type of guitar, like: “How much did Kirk Hammet pay for Greeny?”.
Greeny is a 1959 Gibson Les Paul Standard, named after its original owner, Peter Green. It happened to be purchased by Kirk Hammet, the guitarist of Metallica, which also explains the inclusion of the question “Who is the richest member of Metallica?”, which has nothing to do with guitars at all.
But if we think about this information as being derived from entities that are related to one another, the inclusion of these “People also ask” queries make sense.
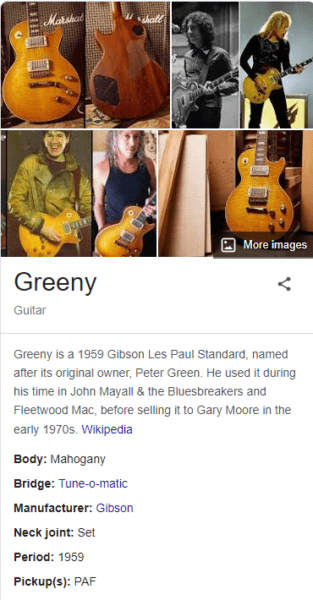
And if we search for “Greeny guitar”, we’ll get a Knowledge Panel conveying some of the attributes of this particular guitar, including the fact that its manufacturer is “Gibson”.
Leverage Schema Markup to Improve Your Semantic SEO
There are many things you can do to implement semantic SEO. A lot of it involves creating clusters of content surrounding the topic that you want to be known for.
However, in addition to this, you need to ensure search engines understand what your content is about and how the entities in your content are connected. Implementing Schema Markup allows you to categorize entities and explicitly relate them to each other, providing search engines with helpful contextual information about your content.
Schema Markup, also known as structured data, is a standardized vocabulary that search engines analyze to understand the content on your web pages. By implementing Schema Markup through code, such as JSON-LD, search engines can contextualize your content and present it to users searching for relevant and related topics.
While machines don’t interpret information like humans do, Schema Markup helps bridge the gap. It does this by providing explicit details about the content on your pages, ensuring search engines accurately comprehend the topics of information your website offers.
One of the most common uses of structured data is the application of the Schema.org vocabulary expressed in JSON-LD. It’s usually found under the “technical SEO” umbrella, and most would know it as the “Thing” responsible for rich results.
Rich results can drive higher click-through rates with their engaging visuals, but if that’s the extent of your Schema Markup application, your semantic SEO strategy is missing out!
So how can you leverage Schema Markup to improve your semantic SEO?
1. Implement more specific Schema Markup to clearly explain what your page is about
To be semantic, search engines need to clearly understand your content.
Content publishers often use generic Schema Markup plugins to add default Schema Markup on certain pages like blog articles, product pages, home page, etc. However, the downside of doing this is the lack of control over your Schema Markup.
Generic Article markup autogenerated by plugins won’t give your content the richly descriptive Schema Markup that best supports the search engines.
Plugins are usually CMS-specific and tend to map more general properties to available metadata (like author, or datePublished). While these properties are still helpful, they don’t describe the content with as much depth as more specific properties like about or mentions, which can be used to call out topics and entities in an Article.
Your markup will also often be disconnected. Each page may have Schema Markup describing the content, but not necessarily how that content relates to other pages across your website.
2. Add @ids in your Schema Markup
Your Schema Markup can be generated and authored without including identifiers (@id). Search engines like Google will still read it and make it eligible for rich results.
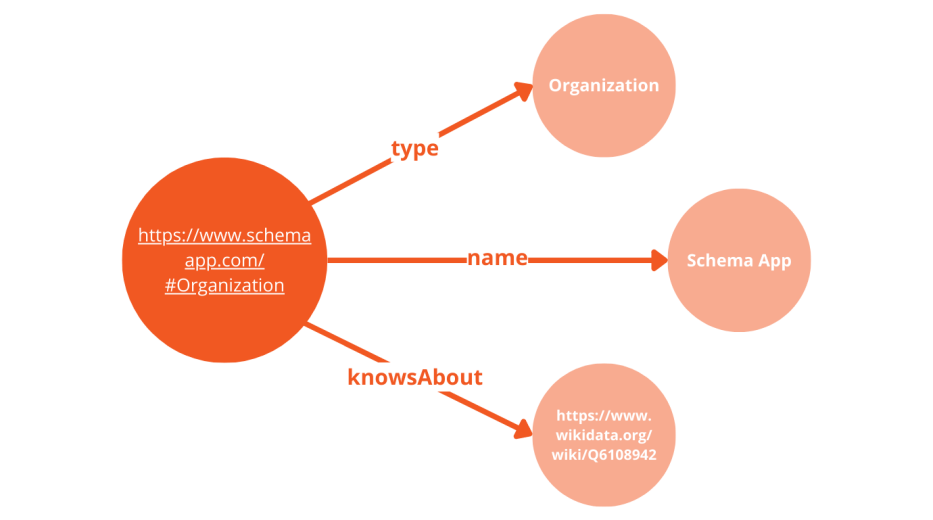
In the JSON-LD syntax, @id is used to provide URIs (uniform resource identifiers) to entities in your Schema Markup. These identifiers allow you to refer back to entities as you build your knowledge graph.
In the example below, the Organization entity created for Schema App’s homepage has the @id “https://www.schemaapp.com/#Organization”. If a blog post on another page wants to say that it was published by the Organization Schema App, the Schema Markup for that page would say the publisher is “https://www.schemaapp.com/#Organization”.
@ids give the entities in your markup unique identifiers.
Think of it like your social insurance number! There may be 10 different people named “Jane Doe” in your organization, but each of them will have a unique ID that differentiates them. Schema App auto-generates @ids for every entity, so you can link the unique entities across your website.
Therefore, if you want to improve your semantic SEO, you should add @ids to your JSON-LD Schema Markup.
3. Connect your Schema Markup to develop your knowledge graph
Establishing a connection between your Schema Markup elements is crucial for developing a comprehensive knowledge graph. Knowledge graphs are necessary for describing how things on your site are related to each other, as well as other things on the internet.
It makes your content more semantic and provides search engines with contextual knowledge about your content.
Connect Your Entities On Your Website
On your website, you can connect different entities to one another. For instance, if you have a law firm with multiple service pages, it’s important to connect those service pages to your organization. This indicates that your organization provides all of those services despite them being on separate pages.
To ensure accurate representation, it’s vital to describe the relationships between marked-up entities in detail. For example, you need to clarify if an article is about a specific topic or if it simply mentions it.
Schema App offers a free Schema Path tool that helps identify available properties to connect your entities effectively.
Connect Entities to External Authoritative Knowledge Bases
You can also connect entities on your site to external authoritative knowledge bases such as Wikidata or Wikipedia. By doing so, you are clearly explaining what your entity is about.
For example, let’s say your page talks about football. Football can mean two different sports to different readers. In America, football is American football while in Europe, football is soccer.
So if your page is about American football, you can link it to the Wikidata entity (https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q41323) for American football in your Schema Markup using the sameAs property. This will help search engines understand that your page is referring to American football and reduces the risk of misinterpretation.
By connecting entities on your site to other entities and external knowledge bases, you are forming your own knowledge graph. The @ids that we mentioned earlier clearly identify the entities in your content, allowing you to connect them and build context.
With Schema App, you have the flexibility to add these entities either manually through our Editor or automatically through the Highlighter, utilizing the Linked Entity Recognition feature. For WordPress users, our WordPress plugin can automatically identify and link entities that you have included in your tags and categories.
Download our Guide to Connected Schema Markup to learn how to connect the entities on your site and build your knowledge graph.
The Future is Semantic
When creating website content for SEO, it’s important to prioritize semantic SEO that focuses on topics rather than just keywords. Search engines now understand context, relationships, and user intent better than ever before.
To stay competitive on SERPs, you need to create relevant, high-quality content that targets specific topics and use connected Schema Markup to help search engines understand how your content relates to user intent, search queries, and other information on the internet.
By embracing semantic SEO, you align your strategy with search engines’ evolving understanding. This leads to better visibility on the SERP and the delivery of highly-tailored content to your target audience.
If you’re looking to implement connected Schema Markup at scale for your site, get in touch with our team to learn about our solution.